Corporate Tax in UAE: Key Strategies for Your Business
- GTAG

- May 12, 2025
- 12 min read
Navigating the New Corporate Tax Landscape in UAE

The UAE's introduction of corporate tax represents a significant shift for businesses. Understanding these changes is crucial for thriving in this evolving market. This guide will outline the key aspects of the new tax system and its implications for businesses of all sizes. This new system marks a departure from the UAE's previous tax environment, which largely exempted businesses from federal corporate tax.
Historically, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) maintained a low corporate tax environment. Until 2023, there was no federal corporate tax except for specific sectors like oil and gas. However, this changed with the introduction of a 9% federal corporate tax in 2023 for companies with taxable profits exceeding AED 375,000. Profits below this threshold remain untaxed. This change aligns the UAE with international standards while diversifying government revenue. For a deeper dive, learn more about UAE corporate tax.
Understanding the Scope of Corporate Tax
This new tax structure presents important considerations for businesses operating in the UAE. Which entities are subject to this tax? What are the implications for free zones? How does this affect businesses of different sizes? Addressing these questions requires a clear understanding of the specific regulations.
Taxable Entities: Generally, businesses exceeding the AED 375,000 profit threshold are subject to the 9% corporate tax. This includes both resident and non-resident companies earning income from activities within the UAE.
Free Zone Considerations: While many free zones retain tax benefits, it's crucial to understand the specific regulations within each zone. Some activities within free zones might still fall under the corporate tax framework.
Impact on SMEs: The zero-tax rate for profits below AED 375,000 significantly benefits small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), enabling them to reinvest profits and drive growth.
Positioning Your Business for Success
Adapting successfully to the new tax environment requires careful planning and understanding the available resources. Businesses should evaluate their current structure, financial planning, and compliance procedures. For additional resources, you might find this helpful: Check out our guide on sitemaps.
Financial Planning: Accurate financial forecasting and budgeting are essential in this new tax environment. Businesses must factor tax liabilities into their projections to maintain profitability.
Structure Evaluation: Reviewing and potentially restructuring your business’s legal structure could optimize your tax position.
Compliance Procedures: Implementing robust record-keeping and reporting systems is critical for complying with the new regulations and avoiding penalties.
This new corporate tax environment necessitates adaptation and strategic planning for businesses in the UAE. By understanding the scope of the tax and implementing proactive measures, businesses can successfully navigate this change and maintain a competitive edge within the UAE market.
Breaking Down UAE Tax Rates: What You Actually Pay
Understanding the UAE's corporate tax system is essential for sound financial planning. This section clarifies the progressive tax structure, from the zero-rate threshold to the standard rate. We'll explore how different profit levels impact your tax liability and examine industry-specific variations.
Decoding the Progressive Structure
The UAE corporate tax system uses a progressive approach. This means different profit levels are taxed at different rates. The system supports smaller businesses while ensuring larger corporations contribute appropriately.
Zero-Rate Threshold: Businesses with profits up to AED 375,000 benefit from a 0% tax rate. This is a substantial advantage for startups and SMEs.
Standard Rate: Profits exceeding AED 375,000 are subject to a standard 9% corporate tax rate. This is a critical number for your financial projections.
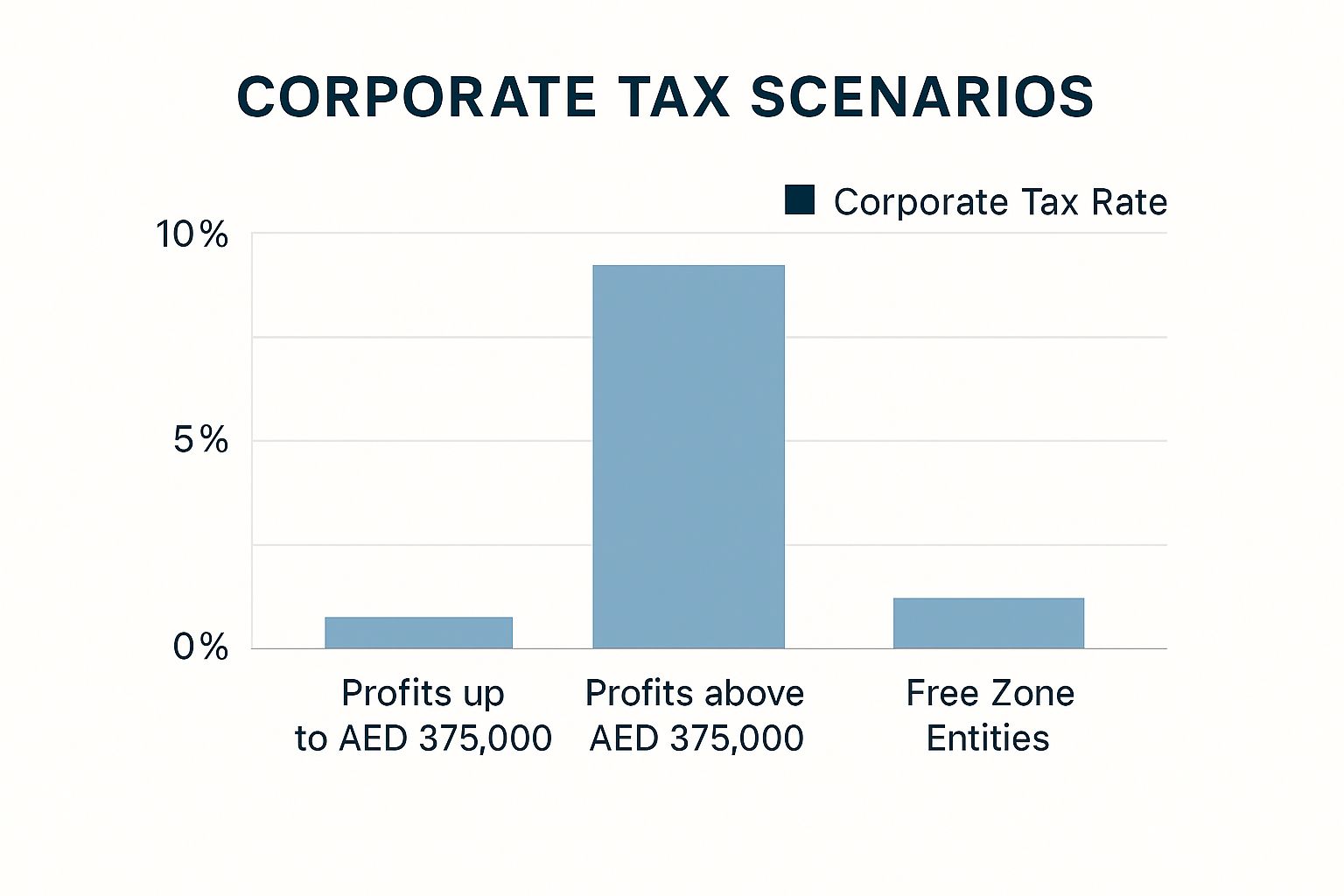
This infographic illustrates the three key corporate tax scenarios in the UAE: the 0% rate for profits up to AED 375,000, the standard 9% rate for profits above this threshold, and the continued 0% rate for qualifying free zone entities. The structure encourages growth while applying a reasonable rate for larger enterprises.
Industry-Specific Variations
While the general corporate tax rate is 9%, some industries have unique provisions. Understanding the specific rules for your sector is vital for accurate tax calculations.
Free Zone Entities: Many free zone companies maintain a 0% tax rate, enhancing their competitive advantage. Confirming the specific regulations for your free zone activity is essential.
Banking Operations and Natural Resource Companies: These sectors might have different tax treatments. Seeking expert tax advice specific to your industry is crucial.
The introduction of the 9% corporate tax represents the highest rate in the UAE's recorded history. The average rate from 2003 to 2025 was approximately 1.17%, highlighting the UAE's historically low corporate tax environment. This new regime aims for global competitiveness, especially considering many economies have corporate tax rates above 20% or even 30%. This makes the UAE an attractive location for multinational corporations. Find more detailed statistics here. Understanding tax implications when selling a business is also important. Read more about the Selling Business Tax Implications. You might also be interested in how to master sitemaps.
To highlight the competitive positioning of the UAE's tax framework, let's examine the following comparison:
UAE Corporate Tax Rate Comparison
This table compares UAE corporate tax rates with other major global economies.
Country/Region | Standard Corporate Tax Rate (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
UAE | 9 | 0% for profits up to AED 375,000 |
USA | 21 | Federal rate; state taxes vary |
China | 25 | |
UK | 19 | |
Germany | Approximately 30 | Includes municipal trade tax |
Japan | Approximately 23 |
This table demonstrates the UAE’s competitive tax rate, particularly for businesses with profits below the AED 375,000 threshold. While other major economies have significantly higher standard corporate tax rates, it’s important to consider the specific tax laws and regulations within each jurisdiction.
Careful analysis of your business structure and profit projections is key to optimizing your tax position in the UAE. Understanding these complexities is a significant step toward financial success in this dynamic market.
Unlocking Tax Exemptions: Hidden Opportunities for Savings

Smart businesses in the UAE understand that minimizing their corporate tax liability requires a deep understanding of available exemptions. This involves exploring deductions, relief measures, and strategic opportunities within the UAE corporate tax framework. Let's delve into how you can maximize your savings.
Navigating Free Zone Advantages
Free zones in the UAE offer significant tax advantages. However, not all free zone activities automatically qualify for preferential treatment. Understanding which activities qualify is crucial for tax optimization.
For instance, certain manufacturing or trading activities within a free zone may retain full exemptions. Others might fall under the standard 9% corporate tax regime. Carefully selecting your free zone and business activity is vital for minimizing your tax burden. You might be interested in: How to master sitemaps.
Government-Linked Entities and Tax Status
Government-linked entities (GLEs) operate within a unique tax landscape. These entities often have specific exemptions or different tax treatments compared to standard businesses.
The relationship between the GLE and the government can influence the applicable tax regulations. Therefore, it's essential for GLEs to clearly understand their tax status to ensure compliance and optimize their tax position.
Strategic Tax Planning for Business Expenses
Optimizing allowable business expenses plays a key role in reducing your overall tax liability. Understanding which expenses are fully deductible, partially deductible, or non-deductible allows for strategic spending management.
This includes leveraging capital allowances and loss carry-forwards. Capital allowances permit businesses to deduct a portion of their capital expenditures. Loss carry-forwards enable them to offset past losses against future profits, further reducing their tax burden.
Specialized Provisions for Startups and SMEs
Startups and SMEs in the UAE can benefit from several specialized tax provisions. Many of these opportunities are often overlooked, leading to potential missed savings.
These provisions may include tax holidays, reduced tax rates for specific periods, or grants for specific activities. Businesses should proactively explore these options to take full advantage of all available benefits.
Practical Examples of Tax Savings
Many businesses have successfully minimized their corporate tax in the UAE through strategic planning. For example, a manufacturing company within a qualifying free zone might maintain a 0% tax rate.
Another example could be a startup leveraging tax holidays and grants to reduce its initial tax burden. Examining these real-world examples helps businesses identify practical strategies to reduce their corporate tax and reinvest those savings in growth and expansion. This careful planning is critical for long-term success.
Mastering Tax Compliance: From Registration to Filing
Successfully navigating the UAE's corporate tax landscape requires a clear understanding of the compliance process. This section provides a practical guide, walking you through each step, from initial registration to the final filing. We'll cover essential documentation, crucial deadlines, and key strategies to help your business stay compliant and avoid penalties. Learn from experienced tax professionals at GTAG about common pitfalls and practical solutions.
Registering for Corporate Tax in the UAE
The first step towards tax compliance in the UAE is registering with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA). This process officially recognizes your business within the UAE tax system and involves submitting necessary documentation and key information about your operations. Completing this initial step correctly is vital to avoid future complications.
Gather Required Documents: Have your trade license, Emirates ID, and other relevant business documents prepared in advance. This preparation will streamline the registration process significantly.
Submit Accurate Information: Accuracy is key. Ensure all details regarding your business activities, projected revenue, and ownership structure are correct to prevent potential issues down the line.
Meet Registration Deadlines: The FTA sets specific deadlines for registration. Adhering to these deadlines is crucial for maintaining compliance and avoiding penalties. More information can be found on our team sitemap.
Understanding Filing Requirements and Deadlines
Once your business is registered, understanding the subsequent filing requirements and deadlines is paramount. The FTA has established clear timelines for submitting your corporate tax returns. Meeting these deadlines is essential to avoid penalties and ensure a smooth compliance journey.
Prepare Accurate Tax Returns: Your tax return should accurately reflect all your financial information. Errors can lead to audits and penalties, so double-checking is always recommended.
Utilize Electronic Filing Systems: The FTA provides online platforms for submitting tax returns. Familiarizing yourself with these systems will make the filing process more efficient.
Maintain Detailed Records: Keeping comprehensive records of all transactions, expenses, and tax-related documents is crucial for compliance and in case of potential audits.
Implementing Efficient Record-Keeping Practices
Efficient record-keeping is essential for minimizing administrative burdens and ensuring your business is prepared for any FTA reviews. This practice also simplifies the tax filing process and provides a clearer picture of your financial performance.
Digital Record-Keeping: Transitioning to digital record-keeping systems can significantly streamline your processes and make retrieving information easier, especially during tax season.
Organize Financial Documents: Implement a well-organized system for storing invoices, receipts, and other financial documents. This organized approach is essential for efficient tax preparation.
Regularly Review and Update Records: Regularly reviewing and updating your financial records ensures accuracy and reflects the current state of your business.
Structuring Your Tax Function
Businesses have different approaches to managing their tax functions. Some choose to build in-house teams, while others opt to outsource to specialized tax consultants. Each approach presents its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
In-House Teams: Larger companies often have dedicated tax departments. This offers direct control but requires substantial investment in personnel and resources.
Outsourced Specialists: Outsourcing to firms like GTAG provides access to expert knowledge and can be a more efficient approach, especially for SMEs that may lack the resources for a dedicated in-house team.
Gaining Insights into Tax Audits and Reviews
Understanding what tax authorities look for during reviews and audits can help your business maintain compliance. While compliance is always the primary goal, being prepared for a potential audit ensures a smoother process should one occur.
Common Audit Triggers: Certain activities, such as significant fluctuations in revenue or unusual deductions, might trigger an audit. Being aware of these potential triggers can help you prepare.
Preparing for an Audit: Meticulous record-keeping and clear documentation of all transactions significantly simplify the audit process.
Professional Representation: Having professional tax representation during an audit can greatly ease the process and protect your rights.
To assist businesses in understanding key deadlines, the following table provides a helpful overview of the UAE Corporate Tax filing timeline.
UAE Corporate Tax Filing Timeline This table outlines key dates and deadlines for corporate tax compliance in the UAE, helping businesses plan their tax activities throughout the fiscal year.
Activity | Deadline | Applicable Entities | Penalties for Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
Corporate Tax Return Filing | Within 9 months of the end of the financial year | All taxable entities | Varies depending on the specific violation |
This table summarizes the key deadlines associated with corporate tax compliance. Businesses should refer to official FTA guidelines for detailed information.
By understanding the UAE corporate tax compliance process and implementing these practices, businesses can minimize the risk of penalties, optimize their tax position, and contribute to a successful financial future in the UAE.
Reshaping Business Operations for Tax Efficiency

The introduction of the 9% corporate tax in the UAE requires businesses to strategically adapt their operations. This section explores how leading companies are restructuring to thrive in this new tax environment. We’ll discuss practical approaches to financial planning and how businesses are revisiting their core structures for tax optimization. You might be interested in: How to master sitemaps.
Rethinking Financial Planning
Financial planning now demands careful consideration of tax implications. This involves projecting tax liabilities and adjusting budgeting processes. Businesses are also exploring investment opportunities that offer tax advantages.
For instance, companies may explore tax-efficient investment vehicles like Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) or revise pricing strategies to account for the new tax. This proactive approach helps maintain financial stability while maximizing returns.
Revisiting Legal Structures and Locations
Many companies are reevaluating their legal structures. Restructuring as a partnership, Limited Liability Company (LLC), or exploring different free zone options are being considered. Location is also key.
Certain free zones offer significant tax benefits, making relocation a potentially attractive strategy. These structural and locational decisions require careful analysis and expert tax advice to ensure alignment with long-term company objectives.
Adapting Internal Policies
Internal policies often require adjustments to ensure tax efficiency. Expense policies, for example, might need revision to maximize allowable deductions.
Transfer pricing policies for multinational companies are also crucial for regulatory compliance. These internal changes minimize tax burdens and ensure smooth business operations.
Industry-Specific Adaptations
Different industries are adapting to the UAE corporate tax in their own ways. Retail businesses, for instance, might adjust inventory management and pricing models. Professional service firms might explore new billing structures.
Manufacturing companies could reconsider supply chain logistics, while technology companies might explore available Research and Development (R&D) incentives. These industry-specific adjustments are vital for remaining competitive and effectively managing tax liabilities.
Transforming Challenges into Advantages
Several companies have successfully turned tax challenges into strategic advantages. By carefully planning and streamlining operations, they have improved financial management and even strengthened their market position.
Compliance is vital to avoid penalties. For more information, review our guide on how to avoid tax penalties. A company might achieve cost savings beyond tax optimization through strategic restructuring. This proactive approach positions businesses for long-term success in the UAE's evolving economic landscape. By embracing change and making informed decisions, businesses can manage tax obligations and thrive.
Global Tax Strategies for UAE-Based Businesses
For businesses with international operations, UAE corporate tax presents both challenges and opportunities. Successfully navigating cross-border taxation requires a deep understanding of international tax laws and how the UAE interacts with the global financial system.
Leveraging Tax Treaties to Minimize Double Taxation
The UAE has established a wide network of tax treaties. These agreements are designed to prevent double taxation and can significantly lower a company’s overall global tax burden. They establish a framework for how taxing rights are allocated between the UAE and other countries. This helps businesses avoid paying taxes on the same income stream in two different jurisdictions.
For instance, if a UAE-based company generates income in a country with which the UAE has a tax treaty, that treaty might reduce or even eliminate the taxes owed in the other country. This presents a significant advantage for businesses operating internationally.
Navigating Transfer Pricing Compliance
Transfer pricing describes the prices charged for goods, services, or intangible assets exchanged between related business entities. Compliance with transfer pricing regulations is vital for multinational companies operating in the UAE. These rules are designed to ensure fair pricing practices and prevent the shifting of profits to jurisdictions with lower tax rates.
Practical approaches to transfer pricing involve meticulously documenting all transactions and providing clear justifications for pricing decisions. This documentation should be readily accessible in the event of a tax audit. Well-defined transfer pricing policies support business objectives while ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements.
Understanding BEPS and the Global Minimum Tax
The Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) initiative, spearheaded by the OECD, aims to tackle tax avoidance strategies employed by multinational corporations. The Global Minimum Tax, a key component of BEPS 2.0, establishes a minimum tax rate of 15% for large multinational enterprises (MNEs).
These global initiatives present both challenges and opportunities for UAE-based businesses. While the Global Minimum Tax might limit certain tax optimization strategies, it also creates a more level playing field and introduces greater certainty in the realm of international taxation.
Structuring International Transactions and Managing Risks
Multinational companies must structure their international transactions carefully to optimize their global tax position, all while remaining compliant with UAE regulations and applicable tax treaties. This involves understanding concepts like permanent establishment.
A permanent establishment describes a fixed place of business through which a foreign company conducts its business activities. Managing permanent establishment risks is crucial for avoiding unexpected tax liabilities in other countries. This careful planning helps mitigate international tax risks and ensures sustainable growth.
Documentation and Reporting for Cross-Border Operations
Thorough documentation and reporting are essential for managing cross-border tax compliance. Maintaining detailed records of international transactions, transfer pricing policies, and tax treaty applications is vital.
This involves meeting reporting requirements both within the UAE and in other jurisdictions where the business operates. Accurate and timely reporting ensures transparency and helps avoid penalties. It also provides valuable data for strategic tax planning.
Through a structured approach to global tax strategy, UAE-based businesses can successfully navigate the complexities of international taxation, minimize their global tax burden, and achieve sustainable growth in the global marketplace. Contact Gulf Tax Accounting Group (GTAG) today. Our team of expert advisors can provide tailored guidance and support to help you navigate the complexities of international taxation and achieve your business goals.
Article created using [Outrank](https://outrank.so)



Comments